
- #Backcalculation of pavement layer properties 1989 full#
- #Backcalculation of pavement layer properties 1989 software#
- #Backcalculation of pavement layer properties 1989 plus#
Finalement, une analyse de la fiabilite a ete effectuee afin de quantifier I' exactitude du retrocalcul par les RNA.
#Backcalculation of pavement layer properties 1989 plus#
Les travaux ont ete encore plus pousses afin de developper des modules de RNA qui peuvent deceler s'il y a une couche rigide sous la chaussee et calculer aussi directement la duree de vie restante de la chaussee, sans retrocalculer les modules des couches. EVERCALC est un logiciel de retrocalcul telecharge de I' Internet, et ExPaS est un algorithme de retrocalcul developpe a I'interne il est base sur une approche de >. Les RNA retrocalculaient les modules des couches, dans des bassins de deflecion a bruit de fond normal et eleve et montraient une meilleure precision que les autres logiciels, plus particulierement EVERCALC et ExPaS. Les reseaux neuronaux artificiels (RNA) sont utilises comme outil de retrocalcul. Resume : Cet article presente les retrocalculs de modules d'elasticite de chaussees asphaltiques calcules in situ en se basant sur les deflecions mesurees par deflectometre a masse tombante (>) a sept points equidistants.

Key words: asphalt pavement, falling weight deflectometer, backcalculation, remaining life, reliability. Finally, a reliability analysis is performed to quantify the performance of backcalculation using an ANN. Work have been extended further to develop ANN models that can predict a possible rigid layer at the bottom of the pavement and can directly predict the remaining life of the pavement without backcalculating the layer moduli.
#Backcalculation of pavement layer properties 1989 software#
EVERCALC is a backcalculation software downloaded from the Internet and ExPaS is a backcalculation algorithm developed in-house, based on a "search and expand" approach. The ANN is observed to backcalculate layer moduli, both from normal as well as noisy deflection basins, with better accuracy compared with other software, namely, EVERCALC and ExPaS. An artificial neural network (ANN) is used as a tool for backcalculation in this work. The improper interface condition of the binder-stabilized base layer has little influence on moduli of asphalt and subgrade layer.Abstract: Efforts have been made in this paper to backcalculate the in situ elastic moduli of asphalt pavement from synthetically derived falling weight deflectometer (FWD) deflections at seven equidistant points.
#Backcalculation of pavement layer properties 1989 full#
The analysis results demonstrate that assuming full bonding, instead of actual interface conditions of asphalt-stabilized base layer, moduli of stabilized base layers is underestimated, up to 2.5 times smaller than the original values. Finally, the backcalculated layer moduli and the original moduli values were compared.
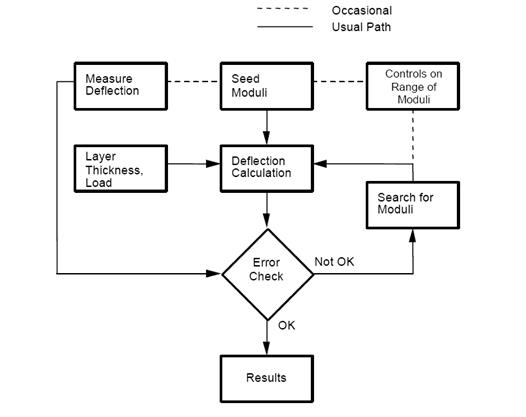
Secondly, different friction coefficient values between asphalt layer and stabilized base layer were introduced into dynamic finite element model, accordingly, deflection basin parameters were calculated and layer moduli are determined based on the established regression functions. Then, the regression functions between deflections basin parameters and layer moduli were created and used to backcalculate layer moduli. Firstly, according to the full bonding hypothesis, a dynamic finite element analysis model was established to generate a synthetic surface deflection database of the semi-rigid asphalt pavements. The objective of this study was to analyze the errors in layer moduli backcalculation due to modeling of layer interface condition. To make appropriate rehabilitation decisions, determining structural layer moduli of the existing semi-rigid asphalt pavements is a crucial task for highway engineers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
